Omega Benefit
$ 61.00
Size: 120 Softgels
Certified Pure Enteric-Coated Anti-Inflammatory Omega-3 Fish Oil Extract
Please select all options.
Highlights:
- Promotes a Balanced Inflammatory Response and Cytokine Levels*
- Helps Reduce Pro-Inflammatory Arachidonic Acid-Derived Eicosanoids*
- Helps the Body Generate Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators*
- Supports Cardiovascular Health*
- Supports Brain Health and Mental Functioning*
- Supports Healthy Glucose and Insulin Metabolism*
Most dietary fats are burned for energy, however our bodies use two specialized types of dietary fat to perform essential functions—omega-3s and omega-6s. Our ancestral diets had balanced levels of these long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), but today the Standard American Diet is loaded with pro-inflammatory omega-6 and deficient in anti-inflammatory omega-3.1 Furthermore, common genetic polymorphisms reduce the conversion of inactive, plant-based PUFAs to their active forms.2
Fish is one of the only concentrated dietary sources of the active omega-3s eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), but overfishing and contaminated stocks make it difficult to safely get enough in our diets. We use certified, contaminant-free fish oil extract with concentrated doses of EPA and DHA in Omega Benefit, for optimal safety and strength.
Hundreds of clinical trials have demonstrated countless benefits for EPA and DHA extracts, including reducing cardiovascular risk,3 increasing insulin sensitivity,4 and promoting brain health.*[5] EPA is potently anti-inflammatory, and has been shown to reduce inflammatory markers and relieve pain in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.*[6-8] DHA is the most important fatty acid in the brain, contributing to fish oil’s powerful neuroprotective benefits which have been shown in numerous studies for depression and cognitive function.*[9-10] Together, EPA and DHA in Omega Benefit provide synergistic support for whole-body wellness.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to treat or cure any disease.
Verified third-party testing and five-star certification from International Fish Oil Standards (IFOS) assures that Omega Benefit has the highest level of purity, potency and stability. Each softgel provides a guaranteed 900 mg of concentrated eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)—the specific omega-3 fatty acid extracts associated with the many health benefits of fish oils. This powerful dose is delivered in a small, enteric-coated softgel for easy swallowing and optimal absorption.
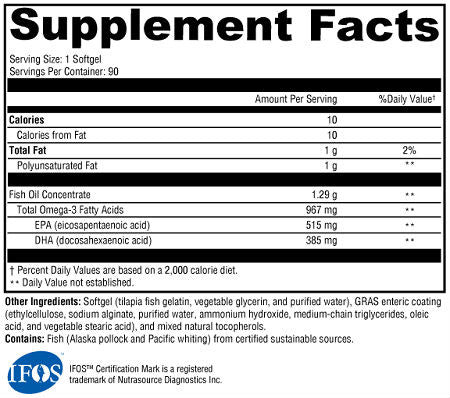
1 SOFTGEL PER SERVING
Fish Oil Concentrate 1.29 g
Total Omega-3 Fatty Acids 967 mg
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) 515 mg
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) 385 mg
Other Ingredients: Softgel (tilapia fish gelatin, vegetable glycerin, and purified water), GRAS enteric coating (ethylcellulose, sodium alginate, purified water, ammonium hydroxide, medium-chain triglycerides, oleic acid, and vegetable stearic acid), and mixed natural tocopherols. Contains: Fish (Alaska pollock, Pacific whiting [sources of fish oil], tilapia [source of fish gelatin]) from certified sustainable sources.
DOES NOT CONTAIN: Wheat, gluten, corn, yeast, soy protein, dairy products, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, egg, GMOs, artificial colors, artificial sweeteners, or artificial preservatives.
Take two softgels daily, or as directed by your healthcare practitioner.
Caution: Individuals taking blood thinners or other medication should discuss potential interactions with their healthcare practitioner.
The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids
Several sources of information suggest that human beings evolved on a diet with a ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 essential fatty acids (EFA) of approximately 1 whereas in Western diets the ratio is 15/1-16.7/1. Western diets are deficient in omega-3 fatty acids, and have excessive amounts of omega-6 fatty acids compared with the diet on which human beings evolved and their genetic patterns were established. Excessive amounts of omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and a very high omega-6/omega-3 ratio, as is found in today's Western diets, promote the pathogenesis of many diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, whereas increased levels of omega-3 PUFA (a low omega-6/omega-3 ratio) exert suppressive effects. In the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease, a ratio of 4/1 was associated with a 70% decrease in total mortality. A ratio of 2.5/1 reduced rectal cell proliferation in patients with colorectal cancer, whereas a ratio of 4/1 with the same amount of omega-3 PUFA had no effect. The lower omega-6/omega-3 ratio in women with breast cancer was associated with decreased risk. A ratio of 2-3/1 suppressed inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a ratio of 5/1 had a beneficial effect on patients with asthma, whereas a ratio of 10/1 had adverse consequences. These studies indicate that the optimal ratio may vary with the disease under consideration. This is consistent with the fact that chronic diseases are multigenic and multifactorial. Therefore, it is quite possible that the therapeutic dose of omega-3 fatty acids will depend on the degree of severity of disease resulting from the genetic predisposition. A lower ratio of omega-6/omega-3 fatty acids is more desirable in reducing the risk of many of the chronic diseases of high prevalence in Western societies, as well as in the developing countries, that are being exported to the rest of the world.
Fish oil supplementation and insulin sensitivity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Background: Fish oil supplementation has been shown to be associated with a lower risk of metabolic syndrome and benefit a wide range of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and several types of cancers. However, the evidence of fish oil supplementation on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity is still controversial. This meta-analysis summarized the exist evidence of the relationship between fish oil supplementation and insulin sensitivity and aimed to evaluate whether fish oil supplementation could improve insulin sensitivity.
Methods: We searched the Cochrane Library, PubMed, Embase database for the relevant studies update to Dec 2016. Two researchers screened the literature independently by the selection and exclusion criteria. Studies were pooled using random effect models to estimate a pooled SMD and corresponding 95% CI. This meta-analysis was performed by Stata 13.1 software.
Results: A total of 17 studies with 672 participants were included in this meta-analysis study after screening from 498 published articles found after the initial search. In a pooled analysis, fish oil supplementation had no effects on insulin sensitivity compared with the placebo (SMD 0.17, 95%CI -0.15 to 0.48, p = 0.292). In subgroup analysis, fish oil supplementation could benefit insulin sensitivity among people who were experiencing at least one symptom of metabolic disorders (SMD 0.53, 95% CI 0.17 to 0.88, p < 0.001). Similarly, there were no significant differences between subgroups of methods of insulin sensitivity, doses of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFA) of fish oil supplementation or duration of the intervention. The sensitivity analysis indicated that the results were robust.
Conclusions: Short-term fish oil supplementation is associated with increasing the insulin sensitivity among those people with metabolic disorders.